TP 7: Simultaneous Polymerization of Twin Monomers with Transition Metal Compounds for Porous Materials Loaded with Metal-/Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles
(2. FP)
Project Manager: Prof. Dr. Heinrich LangTU Chemnitz, Professur für Anorganische Chemie, Chemnitz
Project Goals:
Within the scope of the project “Simultaneous polymerization of twin monomers with transition metal complexes to porous materials
loaded with metal-/metaloxide nanoparticles”, the preparation of nano porous, monolithic compounds, which containing
metal-(M= Ag, Au, Pd, Pt, Rh,…) or metal oxide-NP (NP = nanoparticle) (MxOy= Mn2O3,
Fe3O4, Co2O3, NiO,…) through simultaneous twin polymerization is studied.
The
generation of NPs is caused by the decomposition of metal-oligo-/polyethylen glycol functionalized carboxylates. As twin monomers
for the preparation of the organic and oxidic polymers (SiO2, B2O3, TiO2, …),
tetrafurfuryloxy silane and silicone spiro-compounds, derived from salicylic alcohol are used. Oxidation or carbonization of the
nanocomposites, afford highly porous inorganic or carbon materials, with a narrow pore size distribution and high inner
surface.
- Variation of structural motifs of the starting compounds to generate an universal procedure for the preparation of these porous materials
- Investigation of their heterogeneous catalytic activity (isomerization, hydrogenation, hydroformylation)
The Synthesis of hollow carbon spheres filled with Metal-NPs will be another scope of our project. Therefore, graphitic carbon spheres are filled with the appropriate metal precursor and will be thermally decomposed. A second approach involves initiator-modified metal-NPs, which can undergo a simultaneous twin polymerisation with the corresponding monomers. These materials can also be oxidized or carbonized to obtain silicon dioxide or carbon encapsulated metal-NPs.
- Investigation of nano hybrid capsules regarding the application within medical area or in sensor technology
Results:
Zr- and Hf-containing Twin Monomers
- New twin monomers based on Zr and Hf could successfully be prepared. During the twin polymerization process the prepared Zr monomers were polymerized without any problems, while the Hf compounds showed a phase separation in the hybrid material. This behavior is attributed to the higher content of the inorganic component within these monomers. Copolymerization with established twin monomers leads to amorphous porous SiO2/ZrO2 materials. Additional thermal treatment gave tetragonal ZrO2 and HfO2 nanoparticles in between the siliciumdioxide matrix.
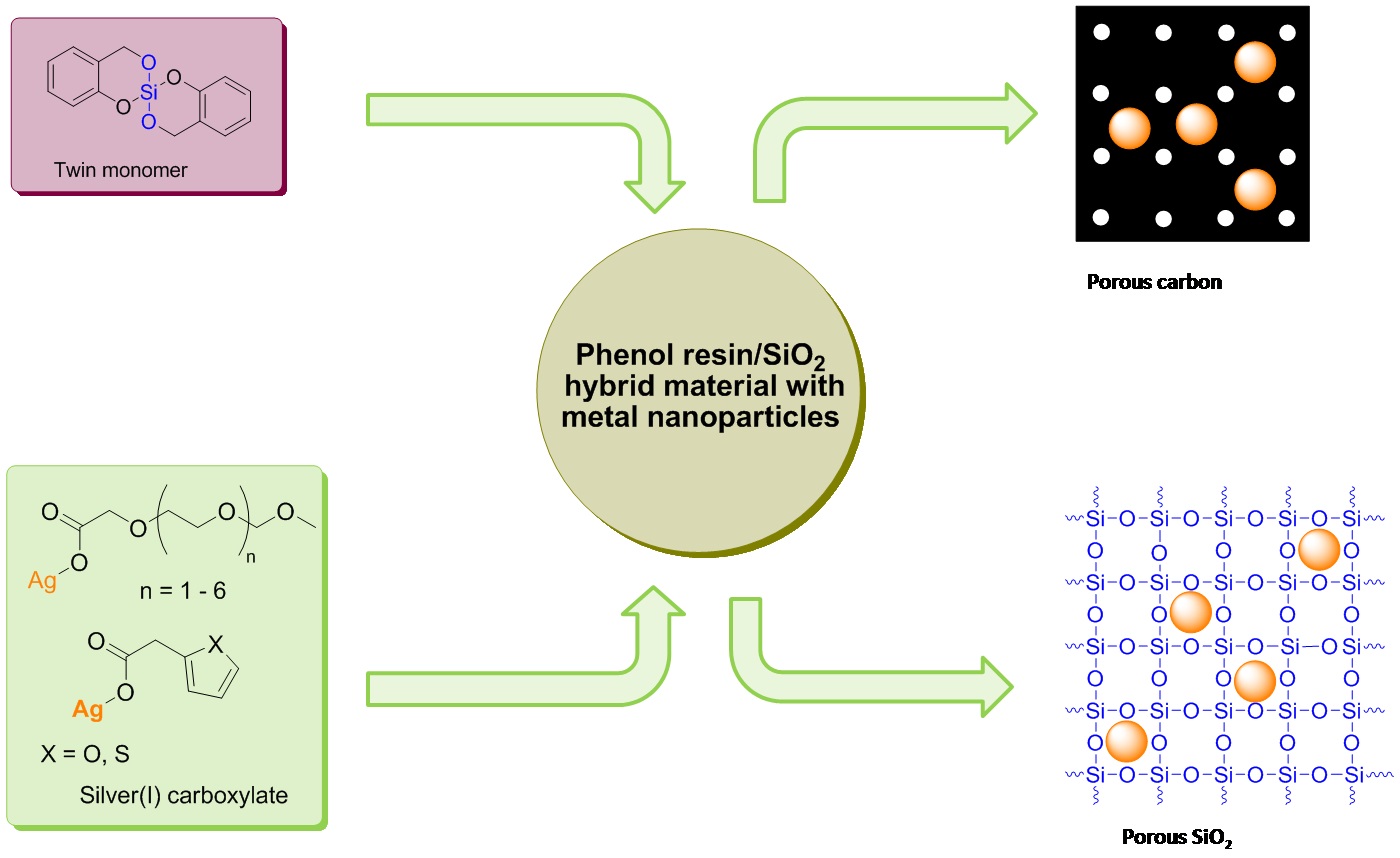
Ag-Nanoparticles via Twin Polymerization
- The development of a suitable precursor made it possible to generate silver nanoparticles in a carbon or siliciumdioxide matrix. Due to twin polymerization homogeneously distributed silver particles with a diameter smaller than 5 nm could be generated. The microporous carbon prevented the nanoparticles from sintering and the high surface-area-to-volume ratio provided excellent requirements for the application in catalysis.
Metal nanoparticle filled carbon hollow spheres
- The modification of established synthesis methods allowed the incorporation of metal nanoparticles in hollow carbon spheres by twin polymerization. Therefore, it could be shown that only with a substrate of a certain diameter the encapsulation takes place during the coating process. Using smaller silica spheres as template, the incorporated nanoparticles were found in cavities formed between connecting hollow carbon capsules. It was possible to generate paramagnetic ironoxide nanoparticle containing carbon hollow spheres. In the case of the silver and gold nanoparticle containing carbon hollow spheres it was possible to show their catalytic activity by a convenient benchmark system.
>>> TP 7 of 2nd Funding Period
